Induced draft vs forced draft – When it comes to ventilation systems, induced draft and forced draft take center stage. Induced draft relies on negative pressure to draw air through the system, while forced draft employs positive pressure to push air through. As we delve into their intricacies, we’ll explore their design principles, applications, efficiency, and environmental impact, providing a comprehensive understanding of these two fundamental ventilation methods.
Induced draft systems, with their inherent ability to handle high temperatures and corrosive gases, find their niche in industrial settings and power plants. Forced draft systems, on the other hand, excel in applications where precise airflow control and low noise levels are paramount, such as in HVAC systems and cleanrooms.
Definition and Explanation
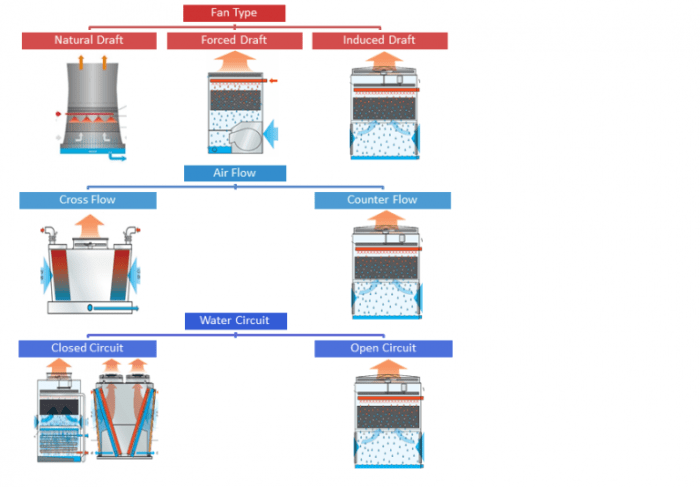
Induced draft and forced draft are two different methods of moving air through a system. Induced draft uses a fan to create a vacuum that draws air through the system, while forced draft uses a fan to push air through the system.
The fundamental difference between the two methods is the direction of airflow. In induced draft, the air flows from the system to the fan, while in forced draft, the air flows from the fan to the system.
Induced Draft
Induced draft is typically used in applications where the system is under negative pressure. This can be beneficial because it helps to prevent the escape of harmful gases or dust from the system.
Forced Draft
Forced draft is typically used in applications where the system is under positive pressure. This can be beneficial because it helps to prevent the entry of unwanted air or contaminants into the system.
Design and Operation
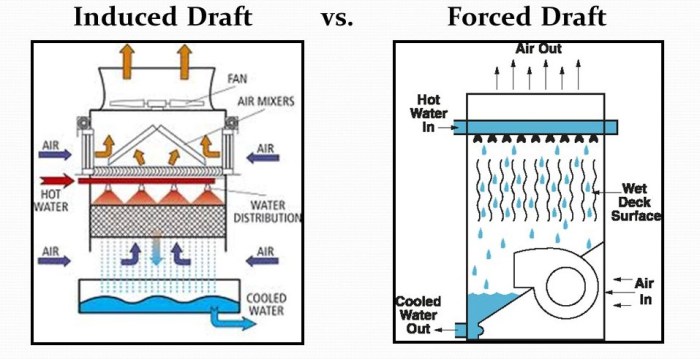
The design and operation of induced draft and forced draft systems differ based on the principles of air movement and the components used.
In an induced draft system, the fan is located at the outlet of the boiler, drawing combustion gases through the system. This creates a negative pressure, which induces the flow of air into the boiler. In contrast, a forced draft system has the fan located at the inlet of the boiler, pushing air into the system.
This creates a positive pressure, which forces the air through the boiler.
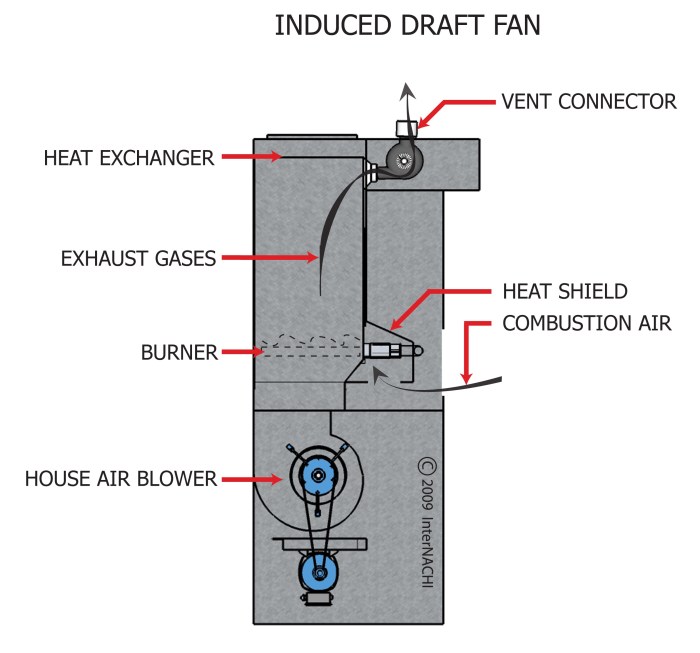
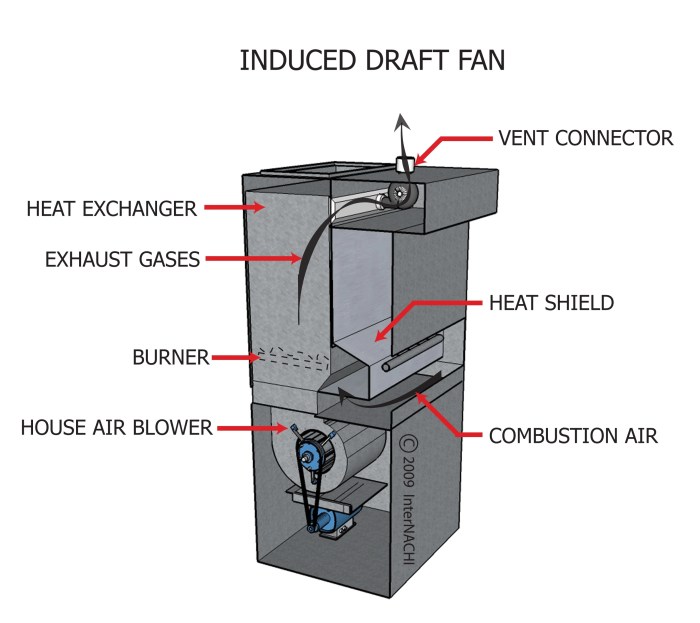
Induced Draft System
The induced draft system relies on the negative pressure created by the fan to draw air into the boiler. The fan is typically located at the top of the boiler, and it draws combustion gases through the boiler and out through the stack.
Induced draft and forced draft are two methods of moving air through a system. Induced draft uses a fan to draw air through the system, while forced draft uses a fan to push air through the system. Induced draft is often used in applications where the air is contaminated, as it can help to prevent the contamination from spreading.
Forced draft is often used in applications where the air is clean, as it can help to improve the efficiency of the system. Brick House Mies Van Der Rohe is an example of a building that uses forced draft to improve the efficiency of the heating and cooling system.
This creates a low-pressure area inside the boiler, which causes air to flow in through the air inlet. The air then passes through the boiler, where it is heated by the combustion gases. The heated air then exits the boiler through the outlet and is drawn out by the fan.
Forced Draft System
The forced draft system uses a fan to push air into the boiler. The fan is typically located at the bottom of the boiler, and it forces air into the boiler through the air inlet. The air then passes through the boiler, where it is heated by the combustion gases.
The heated air then exits the boiler through the outlet and is drawn out by the fan.
Applications and Advantages
Induced draft and forced draft systems are employed in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. Each method offers distinct advantages and benefits, making them suitable for specific requirements.
Induced draft systems are commonly used in applications where there is a need to maintain a negative pressure in the combustion chamber or process area. This negative pressure helps prevent the escape of gases and fumes, ensuring safety and environmental compliance.
Forced draft systems, on the other hand, are preferred when a positive pressure is required to move air or gases through a system. This method is often employed in applications where there is a need for precise control over airflow and pressure.
Advantages of Induced Draft Systems, Induced draft vs forced draft
- Improved combustion efficiency:Negative pressure in the combustion chamber enhances air intake, leading to better fuel combustion and reduced emissions.
- Enhanced safety:The negative pressure prevents the escape of harmful gases and fumes, ensuring a safer working environment.
- Reduced maintenance costs:Induced draft systems generally require less maintenance compared to forced draft systems due to the absence of moving parts in the combustion chamber.
Advantages of Forced Draft Systems
- Precise airflow control:Forced draft systems allow for precise control over airflow and pressure, making them suitable for applications requiring specific air flow rates.
- Reduced energy consumption:Forced draft systems can be more energy-efficient than induced draft systems, especially in applications where a high airflow rate is required.
- Improved durability:Forced draft systems are generally more durable than induced draft systems due to the use of robust components and materials.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption: Induced Draft Vs Forced Draft
Induced draft and forced draft systems differ in their impact on energy efficiency and overall energy consumption.
In an induced draft system, the fan is located at the outlet of the boiler or furnace, drawing combustion gases through the system. This creates a negative pressure, which helps to pull air into the system and maintain combustion. Forced draft systems, on the other hand, use a fan located at the inlet of the boiler or furnace to push air into the system.
This creates a positive pressure, which helps to force combustion gases through the system.
Energy Efficiency
Induced draft systems are generally more energy efficient than forced draft systems. This is because the induced draft fan operates at a lower pressure than the forced draft fan, which requires less energy to operate. Additionally, induced draft systems can take advantage of the natural buoyancy of hot gases, which helps to reduce the amount of energy required to move the gases through the system.
Overall Energy Consumption
The overall energy consumption of an induced draft or forced draft system depends on a number of factors, including the size of the system, the type of fuel being burned, and the operating conditions. However, in general, induced draft systems are more energy efficient than forced draft systems, which can lead to lower operating costs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of both induced draft and forced draft systems.
Maintenance tasks for both systems include regular inspections, cleaning, and lubrication of components such as fans, bearings, and motors. It is also important to check the condition of belts, filters, and ducts to ensure proper airflow and prevent blockages.
Troubleshooting Induced Draft Systems
- Insufficient airflow:Check for blockages in the ductwork, fan blades, or filters. Inspect the fan motor and bearings for any issues.
- Excessive noise or vibration:This could indicate an imbalance in the fan, loose bearings, or a damaged motor. Check the fan assembly and tighten any loose components.
- Motor overheating:Check the motor’s electrical connections and ensure there is no overloading. Inspect the bearings for any signs of wear or damage.
Troubleshooting Forced Draft Systems
- Low air pressure:Inspect the fan blades and housing for any damage or blockages. Check the motor and ensure it is operating at the correct speed.
- Excessive fan speed:This could indicate a problem with the motor controller or a faulty fan. Check the electrical connections and inspect the fan assembly.
- Unusual noises:Noises such as rattling or squealing could indicate loose belts, worn bearings, or a damaged fan. Inspect the system and tighten or replace any faulty components.
Environmental Considerations

Induced draft and forced draft systems have varying impacts on the environment, primarily regarding emissions and air quality.
Induced draft systems typically have lower emissions than forced draft systems because they operate at lower pressures. This results in reduced combustion temperatures, which in turn reduces the formation of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter.
Forced Draft Systems
Forced draft systems, on the other hand, operate at higher pressures, leading to higher combustion temperatures and increased emissions of NOx and particulate matter. However, forced draft systems can be equipped with emissions control devices, such as electrostatic precipitators or scrubbers, to mitigate these environmental concerns.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary difference between induced draft and forced draft?
Induced draft relies on negative pressure to draw air through the system, while forced draft uses positive pressure to push air through.
Which system is more energy-efficient?
Induced draft systems tend to be more energy-efficient, as they utilize the natural buoyancy of hot air to assist in airflow.
What are the typical applications of forced draft systems?
Forced draft systems are commonly used in HVAC systems, cleanrooms, and other applications where precise airflow control and low noise levels are required.