You are studying a population of wild coyotes, embarking on a journey to unravel the intricate dynamics, behaviors, and interactions of these fascinating creatures. From their population size and distribution to their social structure and resource utilization, this exploration delves into the complexities of coyote ecology, offering a comprehensive understanding of their role within ecosystems and their interactions with humans.
Through meticulous observation and analysis, you will uncover the factors influencing coyote population growth and decline, shedding light on the delicate balance between predator and prey. By examining their communication patterns and social hierarchies, you will gain insights into the complexities of coyote behavior and social interactions.
Coyote Population Dynamics
Coyote populations are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of habitats. They are found in North and Central America, and their range has been expanding in recent years. The size and distribution of coyote populations are influenced by a number of factors, including:
Habitat Availability
- Coyotes require access to food, water, and shelter. The availability of these resources can limit the size and distribution of coyote populations.
Prey Abundance
- Coyotes are opportunistic predators that feed on a variety of prey, including rodents, rabbits, deer, and livestock. The abundance of prey can influence the size and distribution of coyote populations.
Human Activity
- Human activity can have a significant impact on coyote populations. Coyotes are often persecuted by humans, which can reduce their numbers. Additionally, human development can fragment coyote habitat and reduce their access to resources.
Environmental Changes
- Environmental changes, such as climate change and habitat loss, can also affect coyote populations. These changes can alter the availability of resources and make it more difficult for coyotes to survive.
Coyote Behavior and Social Structure
Coyotes are social animals that live in packs. The pack is typically led by an alpha pair, which consists of a male and female. The alpha pair is responsible for defending the pack’s territory and raising the young. The rest of the pack consists of subordinate males and females.
Subordinate males and females help to raise the young and defend the pack’s territory.
Communication
- Coyotes communicate with each other using a variety of vocalizations, including howls, yips, and barks. Coyotes also use body language to communicate.
Behavior
- Coyotes are opportunistic predators that feed on a variety of prey. They are also scavengers and will eat carrion. Coyotes are also known to be territorial and will defend their territory from other coyotes.
Coyote Habitat and Resource Utilization
Coyotes are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts. They are also found in urban areas. Coyotes use a variety of resources, including food, water, and shelter.
Food
- Coyotes are opportunistic predators that feed on a variety of prey. They are also scavengers and will eat carrion.
Water
- Coyotes need access to water to survive. They will drink from rivers, streams, ponds, and lakes.
Shelter
- Coyotes use a variety of shelters, including dens, burrows, and caves. Dens are typically located in underground burrows or in the hollow of a tree.
Coyote-Human Interactions

Coyotes are often seen as a nuisance by humans. They can prey on livestock and pets, and they can also be aggressive towards humans. However, coyotes can also be beneficial to humans. They help to control rodent populations and they can scavenge on carrion.
Management Strategies
- There are a number of management strategies that can be used to mitigate conflicts between coyotes and humans. These strategies include:
- Habitat modification
- Exclusion
- Hunting
- Trapping
- Education
Coyote Conservation and Management

Coyotes are an important part of the ecosystem. They help to control rodent populations and they can scavenge on carrion. However, coyotes can also be a nuisance to humans. It is important to find ways to manage coyote populations so that they do not pose a threat to humans or livestock.
Challenges
- There are a number of challenges associated with coyote conservation and management. These challenges include:
- Habitat loss
- Persecution
- Disease
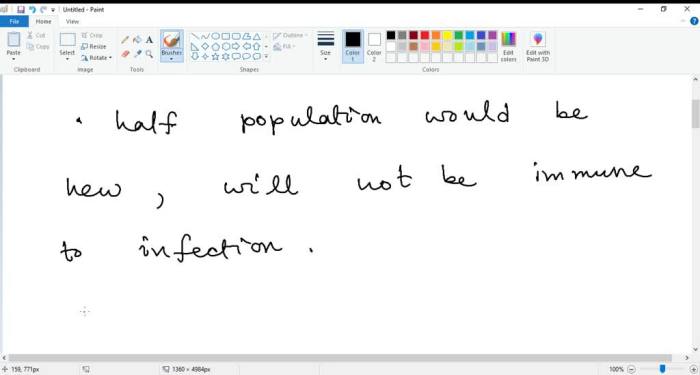
Opportunities, You are studying a population of wild coyotes
- There are also a number of opportunities for coyote conservation and management. These opportunities include:
- Education
- Habitat restoration
- Predator-proof fencing
Helpful Answers: You Are Studying A Population Of Wild Coyotes
What is the average lifespan of a coyote?
Coyotes typically live for 6-8 years in the wild, although some individuals may live up to 13 years.
Are coyotes dangerous to humans?
While coyote attacks on humans are rare, it is important to be aware of their presence and take precautions to avoid conflicts. Never approach or feed coyotes, and keep pets on leashes when in areas where coyotes are known to be present.
What is the role of coyotes in the ecosystem?
Coyotes play a vital role in the ecosystem as predators, helping to control rodent populations and maintain a healthy balance in the food chain.