Plessy v ferguson 1896 answer key – Plessy v. Ferguson 1896 Answer Key unlocks the intricacies of a pivotal legal battle that shaped the course of American civil rights. This comprehensive guide delves into the historical context, legal arguments, and far-reaching implications of this landmark case, providing a thorough understanding of its significance.
The Supreme Court’s ruling in Plessy v. Ferguson established the infamous “separate but equal” doctrine, legalizing racial segregation in public facilities. This decision had a profound impact on African Americans, denying them equal access to education, transportation, and other essential services.
Plessy v. Ferguson Case Overview
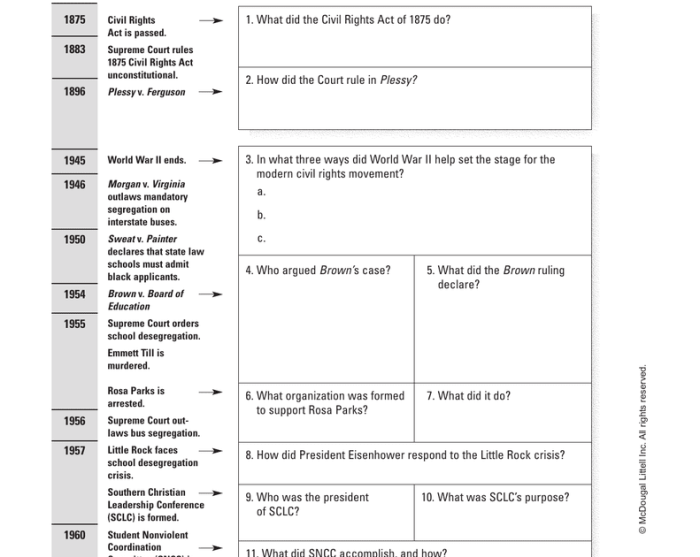
The Plessy v. Ferguson case was a landmark Supreme Court ruling in 1896 that upheld the constitutionality of racial segregation laws for public facilities. This decision had a profound impact on the development of civil rights in the United States.
Legal Arguments
- Plaintiffs:Argued that the Louisiana law violated the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment, which prohibits states from denying any person “the equal protection of the laws.”
- Defendants:Argued that the law was necessary to maintain social order and prevent racial conflict.
Supreme Court Ruling
In a 7-1 decision, the Supreme Court ruled that the Louisiana law was constitutional. The Court held that the law did not violate the Equal Protection Clause because it applied equally to both white and black passengers. The Court also held that the law was not intended to discriminate against black passengers, but rather to promote social order.
Implications
The Plessy v. Ferguson ruling had a devastating impact on civil rights in the United States. The decision legalized racial segregation in public facilities, including schools, transportation, and restaurants. This segregation lasted for decades and contributed to the systemic oppression of African Americans.
Impact on Civil Rights

Immediate Impact
- Legalized racial segregation in public facilities.
- Increased racial discrimination and violence against African Americans.
- Undermined the credibility of the 14th Amendment as a protection against racial discrimination.
Long-Term Effects
- Helped to galvanize the civil rights movement.
- Led to the passage of landmark civil rights legislation, such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
- Continues to be cited as precedent in cases involving racial discrimination.
Dissenting Opinions: Plessy V Ferguson 1896 Answer Key

Justice John Marshall Harlan
Justice Harlan wrote a powerful dissenting opinion in Plessy v. Ferguson. He argued that the law violated the Equal Protection Clause because it was based on race and was intended to discriminate against black passengers. Harlan also argued that the law was harmful to both black and white passengers, as it created a system of racial hierarchy and inequality.
Justice Henry Billings Brown
Justice Brown also wrote a dissenting opinion in Plessy v. Ferguson. He argued that the law was unconstitutional because it violated the Commerce Clause of the Constitution. Brown argued that the law regulated interstate commerce and was therefore beyond the power of the state of Louisiana to enact.
Historical Significance
Plessy v. Ferguson was a turning point in the history of civil rights in the United States. The decision legalized racial segregation and helped to create a system of racial hierarchy and inequality that lasted for decades.
The decision also had a profound impact on the development of the civil rights movement. The movement was inspired by the injustices of Plessy v. Ferguson and other segregation laws, and it ultimately led to the passage of landmark civil rights legislation that outlawed segregation and discrimination.
Plessy v. Ferguson remains a significant case in American history. It is a reminder of the long struggle for racial equality in the United States and the importance of the Constitution as a protector of civil rights.
Legal Analysis
Legal Doctrines and Precedents
- Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment
- Commerce Clause of the Constitution
- Doctrine of separate but equal
Legal Reasoning
The Court’s majority opinion in Plessy v. Ferguson was based on the doctrine of separate but equal. The Court held that the Louisiana law did not violate the Equal Protection Clause because it applied equally to both white and black passengers.
The Court also held that the law was not intended to discriminate against black passengers, but rather to promote social order.
The dissenting opinions in Plessy v. Ferguson argued that the law violated the Equal Protection Clause because it was based on race and was intended to discriminate against black passengers. The dissenting opinions also argued that the law was harmful to both black and white passengers, as it created a system of racial hierarchy and inequality.
Contribution to American Constitutional Law, Plessy v ferguson 1896 answer key
Plessy v. Ferguson is a significant case in the development of American constitutional law. The decision legalized racial segregation and helped to create a system of racial hierarchy and inequality that lasted for decades. The decision also had a profound impact on the development of the civil rights movement.
The movement was inspired by the injustices of Plessy v. Ferguson and other segregation laws, and it ultimately led to the passage of landmark civil rights legislation that outlawed segregation and discrimination.
Questions and Answers
What was the main issue in Plessy v. Ferguson?
The case challenged the constitutionality of a Louisiana law requiring racial segregation in railroad cars.
Who were the key figures in the case?
Homer Plessy, an African American man who was arrested for violating the segregation law, and John H. Ferguson, the judge who upheld the law.
What was the Supreme Court’s ruling?
The Court ruled 7-1 in favor of Ferguson, upholding the “separate but equal” doctrine.