Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive energy potential and kinetic worksheets, meticulously crafted to illuminate the fundamental concepts of energy and its remarkable transformations. Delve into the fascinating world of potential and kinetic energy, unlocking their intricate relationship and practical applications.
Our worksheets are a treasure trove of knowledge, providing a panoramic view of energy concepts. We explore the nuances of potential energy, unraveling its diverse forms and manifestations. Kinetic energy takes center stage, revealing its mathematical essence and dynamic nature.
Through captivating examples, we bring these abstract ideas to life, showcasing objects brimming with potential and kinetic energy.
Energy Potential and Kinetic Concepts
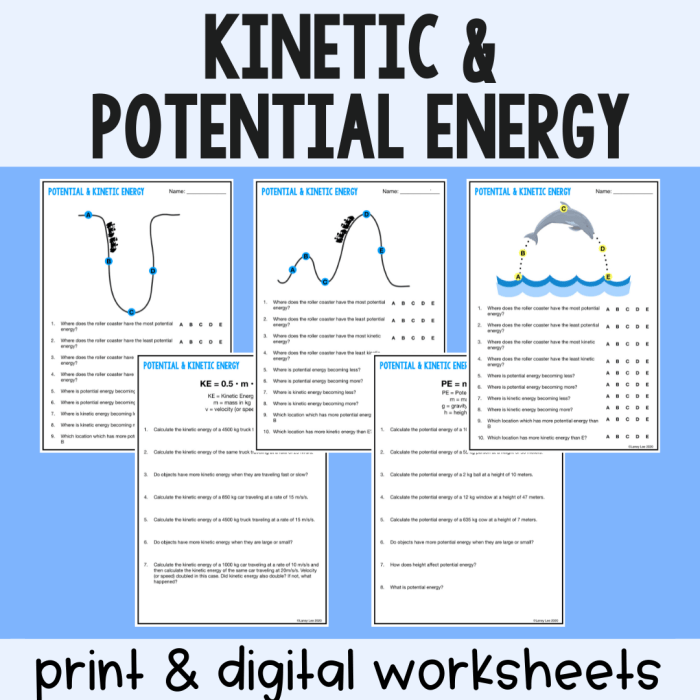
Energy potential and kinetic are two fundamental forms of energy that play a crucial role in our physical world. Potential energy is stored energy due to an object’s position or state, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion. This article explores the concepts, interconversion, and applications of these energy forms.
Forms of Potential Energy
Potential energy exists in various forms:
Gravitational potential energy
Energy stored due to an object’s height or position relative to the Earth’s gravitational field.
Elastic potential energy
Energy stored in deformed objects, such as stretched springs or compressed rubber bands.
Chemical potential energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds, which can be released during chemical reactions.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is calculated using the formula:Kinetic energy = 1/2
- mass
- velocity^2
Examples of Potential and Kinetic Energy
- A rock sitting on a cliff has gravitational potential energy due to its height.
- A moving car has kinetic energy due to its velocity.
- A stretched rubber band has elastic potential energy.
Energy Conversion and Conservation
Potential and kinetic energy can interconvert. For example, when a rock falls from a cliff, its gravitational potential energy converts into kinetic energy.The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy in an isolated system remains constant. This means that energy can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed.
Examples of Energy Transformations
- A hydroelectric dam converts the gravitational potential energy of water into electrical energy.
- A roller coaster converts gravitational potential energy into kinetic energy as it descends.
Worksheets and Problem-Solving
| Energy Type | Formula | Units | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potential energy (gravitational) | PE = mgh | Joules (J) | A ball held at a height |
| Potential energy (elastic) | PE = 1/2kx^2 | Joules (J) | A stretched spring |
| Kinetic energy | KE = 1/2mv^2 | Joules (J) | A moving car |
Practice Problems:
- Calculate the gravitational potential energy of a 2 kg rock sitting 10 m above the ground.
- A car with a mass of 1000 kg is moving at a velocity of 20 m/s. What is its kinetic energy?
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Potential and kinetic energy have numerous applications:
Engineering
Potential energy is used in dams to generate electricity, while kinetic energy is utilized in turbines and engines.
Sports
Potential energy is stored in a drawn bow, while kinetic energy is released when the arrow is shot.
Everyday life
Kinetic energy is involved in walking, running, and driving.
Role in Energy Storage and Power Generation
- Gravitational potential energy is stored in pumped-storage hydroelectric systems for later use in power generation.
- Kinetic energy is harnessed in flywheels for energy storage.
Extensions and Advanced Concepts, Energy potential and kinetic worksheets
Mechanical Energy:Mechanical energy is the sum of potential and kinetic energy. It is conserved in isolated systems without friction or other dissipative forces. Energy Conservation in Complex Systems:The law of conservation of energy applies to complex systems, such as roller coasters or pendulum motion. Resources for Further Exploration:
[Website on energy potential and kinetic energy](https
//www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-physics-1/ap-linear-momentum/energy/a/potential-and-kinetic-energy)
[Book on energy concepts and applications](https
//www.amazon.com/Energy-Concepts-Applications-Benjamin-Crowell/dp/0534402001)
FAQ Summary: Energy Potential And Kinetic Worksheets
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored energy due to an object’s position or condition, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
How can I calculate kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy (KE) is calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 – mass – velocity^2.
What is the law of conservation of energy?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed from one form to another.