Lab 5-7 managing disk quotas – Embark on a journey of disk quota mastery with lab 5-7! In this engaging guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of managing storage space effectively, empowering you to optimize your systems and prevent disk space headaches.
From understanding the fundamentals to implementing advanced techniques, we’ll cover everything you need to know about disk quotas. Get ready to unlock the secrets of efficient storage management!
Understanding Disk Quotas
Disk quotas are a system-level mechanism for managing disk space usage on a computer or network. They allow administrators to set limits on the amount of disk space that individual users or groups can use, preventing them from consuming excessive amounts of storage.
There are two main types of disk quotas: hard quotas and soft quotas. Hard quotas strictly enforce the specified limits, preventing users from exceeding them. Soft quotas, on the other hand, provide a warning when a user approaches the limit, but allow them to continue using space until the hard limit is reached.
Benefits of Using Disk Quotas
- Prevent users from consuming excessive amounts of storage, ensuring that there is enough disk space available for critical applications and data.
- Help to identify users who are using excessive amounts of storage, allowing administrators to take appropriate action, such as providing additional storage or moving data to a different location.
- Improve system performance by preventing users from filling up the disk and causing performance issues.
Limitations of Using Disk Quotas
- Can be complex to manage, especially in large environments with many users.
- Can be difficult to enforce in certain situations, such as when users have multiple accounts or when data is stored on multiple servers.
- Can impact user productivity if quotas are set too restrictively.
Managing Disk Quotas: Lab 5-7 Managing Disk Quotas

Disk quotas are a powerful tool for managing storage usage on your system. They allow you to set limits on the amount of disk space that users or groups can use, helping you to prevent disk space from being overutilized and ensuring that critical data is not lost due to lack of space.
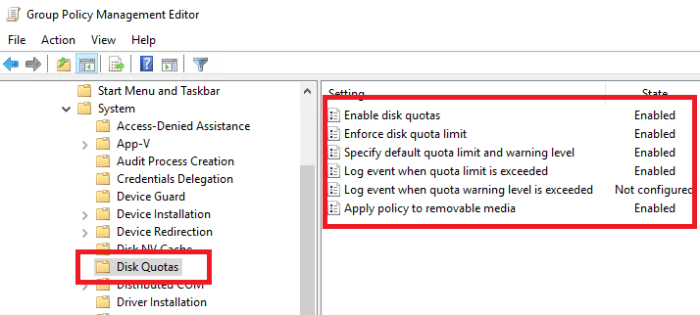
Setting Up and Configuring Disk Quotas
The process of setting up and configuring disk quotas varies depending on your operating system. However, the general steps are as follows:
- Enable disk quotas on your system.
- Create a disk quota for each user or group.
- Set the quota limits for each user or group.
- Enforce the disk quotas.
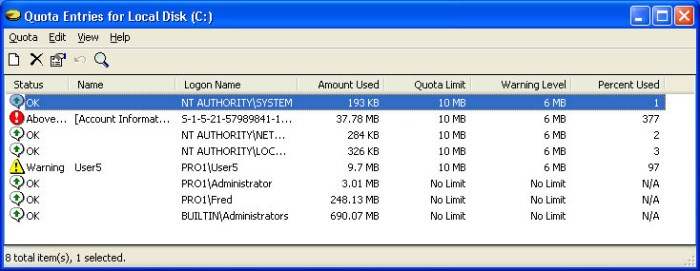
Monitoring and Enforcing Disk Quota Usage
Once you have set up and configured disk quotas, you need to monitor and enforce them to ensure that they are effective. This involves:
- Tracking disk space usage by users and groups.
- Sending notifications to users who are approaching their quota limits.
- Taking action against users who exceed their quota limits, such as suspending their accounts or deleting their files.
Best Practices for Managing Disk Quotas Effectively
To manage disk quotas effectively, you should follow these best practices:
- Set realistic quota limits that are based on the actual storage needs of your users and groups.
- Monitor disk space usage regularly and take action against users who are approaching their quota limits.
- Communicate the disk quota policy to your users and groups so that they are aware of the limits and the consequences of exceeding them.
- Review and adjust the disk quota policy periodically to ensure that it is still meeting your needs.
Troubleshooting Disk Quota Issues
Disk quota issues can arise due to various reasons, causing inconvenience and potential data loss. Understanding these issues and their causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting and resolution.
Identifying Common Disk Quota Issues
Some common disk quota issues include:
- Users exceeding their allocated disk space, resulting in write failures.
- Inconsistent disk quota settings across different systems or users, leading to confusion and data management challenges.
- Misconfiguration of disk quota policies, causing unexpected behavior or errors.
li>Lack of monitoring and timely intervention, resulting in disk quota exhaustion and subsequent data loss.
Resolving Disk Quota Problems
To resolve disk quota issues, consider the following solutions and workarounds:
- Identify and contact users who have exceeded their disk quota. Request them to clean up their files and folders to free up space.
- Review and adjust disk quota settings to ensure they are appropriate and consistent across the system and user groups.
- Troubleshoot and rectify any misconfigurations in disk quota policies to prevent further issues.
- Implement regular monitoring and reporting mechanisms to proactively identify and address disk quota issues before they become critical.
Preventing Disk Quota Issues
To prevent disk quota issues from recurring, consider the following measures:
- Establish clear disk quota policies and communicate them to users.
- Educate users about the importance of disk quota management and responsible data storage practices.
- Implement automated cleanup processes to remove unnecessary or redundant files.
- Monitor disk usage regularly and take proactive measures to prevent quota exhaustion.
Advanced Disk Quota Management

Advanced disk quota management techniques extend the capabilities of basic quota systems, allowing for more granular control and optimization of storage utilization.
One advanced technique is quota inheritance. This allows quotas to be inherited from parent directories or filesystems to child directories and files. This simplifies quota management, ensuring that subdirectories and files adhere to the same quota limits as their parent.
Lab 5-7 on managing disk quotas helps us understand how to control storage space on our systems. Just like in fairy tales where characters often face challenges related to space, such as a princess trapped in a tower or a giant facing a space shortage in his castle ( conventions of a fairy tale ), managing disk quotas ensures that we have enough space for our data and applications, preventing any storage-related setbacks.
Disk Quotas for Storage Optimization
Disk quotas play a crucial role in optimizing storage utilization. By setting appropriate quotas, administrators can prevent users from consuming excessive storage space and ensure that critical applications have sufficient resources.
For example, in a large enterprise environment with thousands of users, implementing disk quotas can help prevent a single user from monopolizing storage space, potentially impacting the performance of essential business applications.
Specific Scenario Examples
Disk quotas can be used in various specific scenarios to enhance storage management:
- User-specific quotas:Assign quotas to individual users to control their storage consumption and prevent unauthorized usage.
- Project-based quotas:Establish quotas for specific projects or departments to ensure fair allocation of storage resources.
- Temporary quotas:Implement temporary quotas for short-term projects or events, allowing users to exceed their regular quotas for a limited period.
- Grace periods:Configure grace periods after quotas are reached, providing users with a buffer time to address storage issues before facing penalties.
Case Study: Disk Quota Management in a Large Organization

Disk quotas play a crucial role in managing storage resources in large organizations. Let’s explore a real-world example and discuss best practices for effective disk quota management.
Challenges
Implementing disk quotas in a large organization presents several challenges:
- Managing user expectations:Users may resist disk quotas, perceiving them as restrictions on their productivity.
- Setting appropriate limits:Determining the optimal disk quota limits for different user groups can be complex.
- Monitoring and enforcement:Tracking disk usage and enforcing quotas effectively requires robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms.
Successes, Lab 5-7 managing disk quotas
Despite the challenges, implementing disk quotas in a large organization can yield significant benefits:
- Optimized storage utilization:Disk quotas prevent users from hoarding excessive data, maximizing storage utilization.
- Cost savings:By optimizing storage usage, organizations can reduce storage costs.
- Improved data security:Disk quotas help prevent data loss by ensuring that users cannot store sensitive data beyond their allocated limits.
Best Practices
To effectively manage disk quotas in a large organization, consider the following best practices:
- Communicate and educate:Clearly communicate the purpose and benefits of disk quotas to users.
- Establish clear policies:Define clear policies for disk quota limits, monitoring, and enforcement.
- Implement a flexible quota system:Allow for flexibility in setting quotas based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Use automated tools:Leverage automated tools for monitoring disk usage, sending notifications, and enforcing quotas.
- Monitor and adjust:Regularly monitor disk usage patterns and adjust quotas as needed to ensure optimal utilization.
FAQ
What are the benefits of using disk quotas?
Disk quotas provide numerous benefits, including preventing storage overages, promoting responsible resource allocation, and facilitating system performance monitoring.
How do I monitor disk quota usage?
Monitoring disk quota usage is crucial. Utilize tools like ‘df -h’ and ‘du -sh’ to track disk space consumption and identify potential issues.
What are some best practices for managing disk quotas effectively?
Best practices include setting appropriate quotas, monitoring usage regularly, enforcing limits, and providing clear communication to users about disk quota policies.